You will see roller bearings are stronger than ball bearings for heavy loads. Ball bearings are good for lighter jobs and fast spinning. Strength is important because industries need safe and efficient bearings. Smart bearings with sensors help check their condition. Companies like E-ASIA use advanced roller bearings in electric cars and machines. Materials like ceramic and self-lubricating bearings lower maintenance costs and last longer. When picking a bearing, think about your load and speed needs.
Key Takeaways
Roller bearings are stronger than ball bearings for heavy loads. Pick roller bearings for hard work.
Ball bearings work best when things move fast. Use them if speed matters more than how much weight they hold.
Think about the load type when you pick bearings. Roller bearings are better for radial loads. Ball bearings can handle some axial loads.
How long bearings last is important. Roller bearings usually last longer under heavy use than ball bearings.
The material you pick changes how well bearings work. Strong materials like steel or ceramic make bearings stronger and last longer.
You must take care of bearings often. Keep them clean and oiled to help them last and work well.
Know how the designs are different. Roller bearings spread the load over a bigger area. Ball bearings touch at one point.
Always pick the right bearing for your machine. This helps it work best and keeps it from breaking.
Roller Bearing vs Ball Bearing Strength
Direct Strength Comparison
When you look at roller bearings and ball bearings, you can see they are different in strength. Roller bearings have rollers that spread force over a bigger area. Ball bearings have small balls that touch the raceway at just one spot. This lets roller bearings hold heavier loads without bending or breaking. Ball bearings are better for lighter loads and fast spinning.
Tip: Radial load is when the force pushes sideways on the bearing. Axial load is when the force pushes from the end, along the axis.
Roller bearings are used in machines that carry heavy things, like conveyor belts or truck wheels. Ball bearings are good for things like fans, skateboards, or electric motors. Roller bearings do not bend as much because the load spreads out along the roller. Ball bearings can bend more easily if the pressure is too high.
Load Capacity Differences
You might want to know how much weight each bearing can hold. Roller bearings can hold more weight than ball bearings. This is because rollers touch the raceway in a line, not just one spot. The bigger contact area helps roller bearings support more weight.
Here is a simple table that shows how roller bearings and ball bearings compare in load capacity and how long they last:
Manufacturers also give ratings for different loads. You can see the main differences in this table:
Type of Bearing | Radial Load Capacity | Axial Load Capacity | Combined Load Capacity |
Ball Bearings | Moderate to high | Moderate | Varies by design |
Roller Bearings | High | Moderate to high | Efficient for both |
Roller bearings are better for radial loads. Ball bearings can handle some axial loads, especially if you use angular contact ball bearings. Roller bearings work well for both types of loads, even in hard jobs.
Roller bearings can carry more radial load because of their shape and bigger contact area.
Ball bearings can take some thrust loads, but roller bearings are better for heavy loads.
Angular contact ball bearings can take higher combined loads than single row ball bearings.
Structural Rigidity
You should think about how stiff a bearing is. Roller bearings are stiffer than ball bearings. This is because rollers touch the raceway in a line. Ball bearings only touch at one point, so they are less stiff.
Roller bearings have more rolling parts to help support the load, which makes them stiffer.
The type, size, and space inside the bearing can change how stiff it is.
Roller bearings are less likely to bend or change shape under heavy loads.
You find roller bearings in places where you need strong support and little movement, like in big machines.
Roller bearings can also handle shocks and small mistakes in alignment better than ball bearings. They last longer and are less likely to get damaged when used for tough jobs.
Roller Bearing Construction
Design Features
Roller bearings have special parts that make them strong. Engineers pick tough materials like steel or ceramic for these bearings. These materials help the bearings last longer and not break easily. The shape of the rollers matters a lot. Some rollers are straight, and some are shaped like barrels or are tapered. These shapes help spread out the force and lower stress on one spot.
Manufacturers use smart tools to test roller bearing designs. They use computers to see how the bearing handles stress. This is called finite element analysis. It helps them find weak spots and make the bearing better. Special coatings are also used on the surface. These coatings lower friction and protect the bearing from wearing out.
Note: Roller bearings often have seals to keep out dust and dirt. This helps them work well in hard places.
Here are some important design features to know:
Picking the right material makes bearings stronger.
The shape of the roller helps spread out the load.
Load ratings help you choose the best bearing.
Computer tests help find and fix weak spots.
Special coatings lower friction and stop wear.
All these things work together to make roller bearings strong for hard jobs.
Contact Area and Load Distribution
Roller bearings and ball bearings handle force in different ways. Roller bearings have rollers that touch the raceway in a line. This line contact spreads the load over a bigger area. Ball bearings only touch at one point, so the force is on a small spot.
The bigger contact area in roller bearings lets them hold more weight. Each part of the bearing feels less stress. This design helps the bearing last longer and not break from shocks. Roller bearings can take hits better than ball bearings.
Roller bearings use special systems to keep working well. Lubrication systems lower friction and heat. This helps the bearing work even in tough places. Seals keep out dirt and water, so the bearing stays clean and works well.
Roller bearings can carry heavy weights.
Tough materials help them last and not rust.
Self-aligning designs let them work if the shaft is not perfect.
They can take shocks and protect other parts.
Seals keep out dirt for a longer life.
Tip: If you need a bearing for heavy loads or rough jobs, roller bearings are a good pick. Their design helps them stay strong and last a long time.
Ball Bearings Explained
Design and Mechanics
You will find that ball bearings have a simple but clever design. Each ball bearing uses small, round balls as rolling elements. These balls sit between two rings called raceways. When you spin the bearing, the balls roll smoothly and reduce friction. This design helps machines move with less effort.
Here is a table that shows the main differences between ball bearings and roller bearings:
Feature | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
Rolling Element | Spherical balls | Cylindrical, tapered, or spherical rollers |
Contact Area | Smaller contact area, higher point loads | Larger contact area, distributes load better |
Types | Deep groove, angular contact, thrust | Cylindrical, tapered, spherical roller |
Ball bearings use point contact. This means each ball touches the raceway at just one spot. Because of this, ball bearings can spin very fast. You often see them in electric motors, fans, and bicycles. Ball bearings come in different types, such as deep groove, angular contact, and thrust. Each type works best for certain jobs.
Note: Ball bearings work well for light to moderate loads and high speeds. You should pick them when you need smooth, fast movement.
Precision and Deformation
Ball bearings give you high precision. The balls and raceways fit together tightly. This tight fit helps the bearing spin with little wobble. You get smooth and quiet operation. Machines that need accuracy, like hard drives or dental tools, often use ball bearings.
You should know that ball bearings have a smaller contact area. The balls touch the raceway at a single point. This design can lead to higher stress at that spot. If you put too much weight on a ball bearing, the balls and raceways can deform. Deformation means the balls or rings change shape. When this happens, the bearing may not work well.
Ball bearings handle light to moderate loads best.
Too much force can cause dents or flat spots on the balls.
Ball bearings can lose precision if they deform.
Roller bearings use rollers instead of balls. The rollers touch the raceway along a line, not just a point. This line contact spreads the load and lowers stress. Ball bearings, with their point contact, can wear out faster under heavy loads.
You should choose ball bearings when you need speed and accuracy. If your machine faces heavy loads, roller bearings may last longer. Always match the bearing type to your needs for the best results.
Load Handling
Radial Loads
Machines sometimes need to hold weight from the side. This force is called a radial load. Bearings help control these side forces. Roller bearings are good for heavy radial loads. The rollers touch the raceway in a line. This spreads the force over more space. It makes the bearing stronger and helps it last longer. Ball bearings use balls that touch at one spot. They are better for lighter radial loads. You see ball bearings in fans, skateboards, and electric motors. These machines do not carry heavy side weight. Roller bearings work best in conveyor belts, truck axles, and other tough jobs.
Tip: If your machine has strong side forces, use roller bearings. They give better support and last longer.
Axial Loads
Axial loads push straight along the shaft. This happens when something presses or pulls through the center. Not all bearings handle axial loads the same way. Some types are better for this job. Here is a table that shows how bearings handle axial loads:
Bearing Type | Axial Load Capacity Description |
Axial Cylindrical Roller Bearings | High axial load carrying capacity, very stiff, supports force in one direction. More load capacity than axial needle roller bearings of the same size. |
Angular Contact Ball Bearings | Made to hold big axial loads in one direction and also handle radial loads because of their contact angle. |
Axial cylindrical roller bearings are strong for one-way axial loads. They stay stiff and do not bend much. Angular contact ball bearings can handle both axial and radial loads. Their special shape lets them take more force in one direction. You often see these bearings in pumps, gearboxes, and machine tools.
Combined Loads
Some machines get both radial and axial loads together. This is called a combined load. Bearings need to handle both forces at once. Ball bearings and roller bearings act differently with combined loads. The table below shows how they work:
Bearing Type | Speed Performance | Load Capacity |
Ball Bearings | Best for high-speed jobs | Lower load capacity because of point contact |
Roller Bearings | Not as good for fast spinning | Higher load capacity because of line contact |
Ball bearings spin faster. They are best for speed and lighter loads. Roller bearings hold more weight. They do not spin as fast but last longer with heavy loads. Pick roller bearings for slow, heavy jobs. Use ball bearings for fast, light jobs.
Note: Always choose the right bearing for your machine. The best choice keeps your equipment safe and working well.
Durability and Longevity
Wear Resistance
You want your bearings to last a long time, especially in big machines. Roller bearings and ball bearings do not wear out the same way. Roller bearings use strong materials and special coatings to stop wearing down. Ball bearings are good for lighter work but can wear out faster if the job is hard. Hybrid bearings have ceramic parts and are very good at fighting wear. These bearings still work well even if there is dirt or not enough oil.
Tip: Pick hybrid bearings for machines in dirty or rough places. They last longer than all-steel bearings.
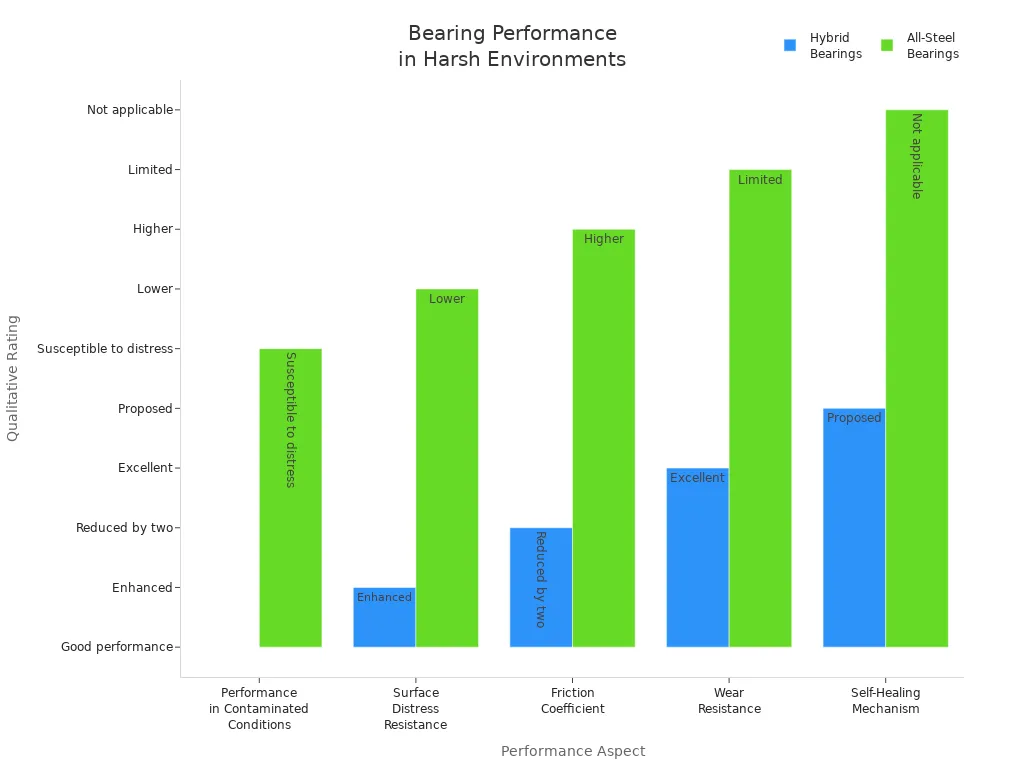
Here is a table that shows how hybrid and all-steel bearings do in tough jobs:
Aspect | Hybrid Bearings | All-Steel Bearings |
Performance in Contaminated Conditions | Good performance in poor lubrication and contaminated conditions | More likely to get damaged early and crack |
Surface Distress Resistance | Better at stopping surface damage | Not as good at stopping surface damage |
Friction Coefficient | Half as much friction as all-steel | More friction than hybrid bearings |
Wear Resistance | Very good at not wearing out in dirty places | Not as good at stopping wear |
Self-Healing Mechanism | May heal themselves because of hard ceramic | Does not heal itself |
Fatigue Life
Fatigue life means how long bearings last before breaking from stress. Roller bearings and ball bearings handle stress in different ways. Roller bearings spread the weight along a line, so they last longer in hard jobs. Ball bearings touch in one spot, so stress builds up faster. Ball bearings have even stress because of their round shape. Roller bearings use a layer model to guess how long they last. Ball bearings use a 3-DOF model for this.
Here is a table that shows how fatigue life is different:
Aspect | Roller Bearings | Ball Bearings |
Internal Stress Cycle | Changes with shape and load | More even because of round balls |
Load Distribution | Uses a layer model for math | Uses a 3-DOF model for math |
Contact Mechanics | Uses Hertzian theory | Also uses Hertzian theory |
Fatigue Failure Mechanism | Breaks by chipping on the raceways | Also chips but may break at a different speed |
Life Prediction | Uses dynamic load capacity to guess | Also uses dynamic load capacity to guess |
Pick bearings with longer fatigue life for big machines. Roller bearings usually last longer in hard jobs. Ball bearings are good for lighter and faster work.
Performance in Tough Environments
Big machines often face shocks, hits, and rough places. Roller bearings are better at handling shocks because they are strong. Ball bearings can get damaged more easily in rough places. Hybrid bearings last a long time in dirty or tough jobs. They do not get damaged easily and keep working even with little oil.
Roller bearings last longer in machines with heavy loads and shocks.
Ball bearings are best for clean and smooth places.
Hybrid bearings last the longest in dirty or rough places.
Note: Always check where your machine will be used before picking bearings. The right bearing lasts longer and saves you money.
Applications
Heavy-Duty Uses
Roller bearings are used in tough jobs with heavy loads. These bearings are strong and last a long time. You see cylindrical roller bearings in mining machines. They are in vibrating screens, conveyor belts, and crushers. Spherical roller bearings help cranes and bulldozers in construction. They handle big impacts and heavy weight. These jobs need strong and reliable bearings.
Cylindrical roller bearings: Used in mining for vibrating screens, conveyor systems, and crushers.
Spherical roller bearings: Found in cranes and bulldozers in construction, facing heavy loads and impacts.
Roller bearings are best when you need to move heavy things safely. Pick them for hard jobs that need strong support and less bending. These bearings help stop breakdowns and keep machines working well.
Tip: Always check the load rating and bearing type for tough jobs. This helps you pick the right bearing for your machine.
High-Speed Uses
Ball bearings work great in machines that spin fast. You find them in motors, turbines, and other fast machines. Ball bearings have small, light parts that lower spinning force. This lets your machines run faster with less stress. Ceramic ball bearings last longer and stay stiff at high speeds.
Here is a table that shows why ball bearings are good for fast machines:
Advantage | Description |
Reduced Centrifugal Loads | Smaller and lighter rolling elements lead to lower centrifugal forces during operation. |
Improved Stiffness | The dynamic behavior of bearings with lighter balls enhances stiffness at high speeds. |
Longer Service Life | Bearings with ceramic rolling elements have a longer service life compared to those with steel elements. |
Pick ball bearings if you want your machines to go fast. These bearings help your equipment last longer and work better. Ball bearings also make machines move smoothly with less friction.
Everyday Machinery
Ball bearings are in many machines you use every day. They are fast, work well, and fit many jobs. Fans, pumps, and farm machines use 6200 Series ball bearings. The 6300 Series is in heavy machines, conveyor belts, and mining tools. R Series ball bearings help drills, electronics, and fans work smoothly.
Here is a table that shows where ball bearing series are used:
Series | Common Use Cases |
6200 Series | Fans, pumps, agricultural machinery |
6300 Series | Heavy machinery, conveyor belts, mining equipment |
R Series | Cordless drills, electronics, ventilation systems |
Ball bearings make machines quieter and more efficient. You see them in many places because they handle speed and work well. When you pick bearings for daily machines, you get less maintenance and steady performance.
Note: Always match the bearing type to your machine’s needs. This helps you get the best speed and performance and ensures long-lasting results.
Choosing the Right Bearing
Key Selection Factors
You need to pick the best bearing for your machine. First, think about what the bearing will do. Some bearings are better for heavy loads. Others are good for fast spinning. Check if the load is radial, axial, or both. Radial loads push from the side. Axial loads push along the shaft. Combined loads use both types of force.
Here is a table to help you compare roller bearings and ball bearings for different jobs:
Factor | Roller Bearings | Ball Bearings |
Load Type and Capacity | Best for heavy radial loads | Good for lighter loads |
Speed Requirements | Usually slower speeds | Great for high-speed jobs |
Lubrication and Maintenance | Needs more checks and oil | Needs less care |
Space and Installation | Takes up more room | Fits in small spaces |
Cost vs Longevity | Costs more but lasts longer | Cheaper but wears out faster |
Think about how much space you have. Roller bearings need more room. Ball bearings fit in tight spots. Maintenance is important too. Roller bearings need more oil and checks. Ball bearings need less care.
Tip: Always choose the bearing that matches your job. Heavy machines need strong bearings. Fast machines need bearings that spin quickly.
When you pick bearings, look at these things:
Load type and capacity: Make sure the bearing can handle your machine’s weight.
Speed requirements: Pick a bearing that works at your machine’s speed.
Lubrication and maintenance: Find out how often you need to check the bearing.
Space and installation: See if the bearing fits in your machine.
Cost vs longevity: Decide if you want to pay more for a bearing that lasts longer.
If you match the bearing to your needs, your machine will work better. This helps your machine run smoothly and last longer.
Cost vs Performance
You want bearings that give you good value. Price is important, but how well the bearing works matters more. Roller bearings cost more. They last longer and work for tough jobs. Ball bearings cost less. They are good for light loads and fast spinning.
Think about how long you want your machine to last. Roller bearings may save money because they last longer. Ball bearings might need to be replaced sooner. Try to balance price and performance. Sometimes, paying more for a strong bearing saves money later.
Here is an easy way to compare cost and performance:
Roller bearings: Cost more, good for heavy loads, last longer.
Ball bearings: Cost less, good for speed, wear out faster.
Note: Always check your budget and what your machine needs. The right bearing keeps your equipment safe and working well.
You can ask a bearing expert if you have a special job. Experts help you pick the best bearing for your machine. Good choices mean fewer problems and better results.
Misconceptions
Size and Strength
You might think that bigger bearings always mean more strength. This is not always true. The type of bearing matters more than just its size. Some people believe that a large ball bearing can handle any heavy load. In reality, the shape and design of the rolling elements play a bigger role.
Roller bearings use rollers that touch the raceway along a line. This line contact spreads the force over a larger area. Ball bearings use balls that touch at a single point. Even if you pick a bigger ball bearing, it may still not handle as much weight as a smaller roller bearing. You should always check the load rating and not just the size.
Remember: A bigger bearing does not always mean a stronger bearing. Always look at the type and design before making your choice.
Load Myths
Many people believe that ball bearings can handle any kind of load because they are common and easy to find. This is a myth. Ball bearings work well for light to moderate loads and high speeds. They do not perform as well under heavy radial loads or strong shocks.
Roller bearings are better for heavy-duty jobs. They can carry more weight without deforming. You might hear that ball bearings are just as strong as roller bearings if you use a bigger size. This is not true. The way each bearing handles force is different.
Here is a table that shows the real advantages and disadvantages of each type:
Bearing Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Ball Bearings | - Low friction for high-speed use
- Compact for small machines
- Can handle both radial and axial loads | - Limited load capacity for heavy radial loads
- Can deform under too much weight
- More sensitive to misalignment and shock |
Roller Bearings | - Higher load capacity
- Handles heavy loads without deforming
- Less sensitive to shock and misalignment | - Higher friction
- Bulkier, needs more space
- May need more maintenance at high speeds |
You should not believe that all bearings work the same way. Ball bearings are great for speed and light loads. Roller bearings are the best choice for heavy loads and tough jobs. Always match the bearing type to your machine’s needs.
Tip: Check the load ratings and the type of bearing before you decide. This helps you avoid problems and keeps your machines safe.
FAQs
Identifying Overload
You may wonder how to spot when bearings face too much stress. Overload can damage both roller bearings and ball bearings. You need to look for certain signs that show the bearing is in trouble. These signs help you catch problems early and prevent bigger failures.
Here is a table that shows the main indicators of bearing overload:
Indicator Type | Description |
Fatigue spalling | Metal breaks away from the raceway because of too much load. |
Handling damage | Dents or nicks from rough transport or installation. |
Cage damage | Skewed or binding rollers when the bearing is dropped or installed wrong. |
Preload/overload damage | Damage from too much force, often leading to fatigue spalling. |
Deformations | Metal flows or rib faces change shape from excess heat, which can lock up the bearing. |
If you see metal flakes, dents, or strange noises, you should check your bearings. Heat and vibration can also warn you about overload. You may notice the bearing feels rough or does not spin smoothly. These signs mean you need to act fast to avoid bigger problems.
Tip: Always inspect your bearings after heavy use or if you notice changes in sound or movement.
Maintenance Tips
You want your bearings to last as long as possible. Good maintenance helps you avoid breakdowns and saves money. You should follow some simple steps to keep your bearings in top shape.
Keep bearings clean and free from dirt or dust.
Use the right lubrication for your bearings.
Watch the temperature and vibration during operation.
Install bearings properly to avoid damage.
Perform regular inspections and maintenance.
You should also avoid running your bearings too fast or with too much weight. Make sure the shaft and housing line up correctly. These steps help prevent early wear and damage.
For ball bearings, you need to check for wear, damage, or contamination. Scheduled maintenance and inspection help you catch problems early. Proper lubrication keeps your bearings running smoothly.
Note: Clean bearings and correct installation make a big difference in how long your equipment lasts.
If you follow these tips, you will get better performance and longer life from your bearings. You protect your machines and avoid costly repairs.
You see roller bearings last longer and handle heavy loads better than ball bearings. Ball bearings work well for high speeds and lighter jobs. The table below shows how roller bearings offer nearly double the life at the same load:
Bearing Type | Load Capacity | L10 Life (hours) |
Ball Bearing (6205) | 5 kN | ≈ 34,000 |
Roller Bearing (NU205) | 5 kN | ≈ 71,000 |
You should match your bearing to your machine’s load and environment. For tough jobs, pick roller bearings. For fast, light work, choose ball bearings. If your application is complex, consider these steps:
Research and vet suppliers.
Communicate your needs clearly.
Check for quality and certification.
Ask about after-sales support.
Picking the right bearing keeps your equipment safe and running longer.
FAQ
How do you know which bearing type to choose for your project?
You should check your load, speed, and space needs. Roller bearings work best for heavy loads. Ball bearings fit high-speed jobs. Always match the bearing to your machine’s job.
What signs show your bearing is wearing out?
You may hear grinding noises or feel rough movement. Heat or vibration can also warn you. Look for metal flakes or dents. These signs mean you should inspect your bearing soon.
Can you mix roller bearings and ball bearings in one machine?
You can use both types in one machine if each fits its job. Roller bearings support heavy loads. Ball bearings help with speed. Always follow the manufacturer’s advice.
How often should you lubricate your bearings?
You should check and lubricate bearings based on your machine’s use. Heavy jobs need more frequent checks. Clean bearings and fresh oil help your equipment last longer.
What happens if you overload a ball bearing?
You may see dents, flat spots, or hear strange noises. The bearing can lose precision and wear out fast. Overloading shortens its life and may damage your machine.
Are ceramic bearings better than steel bearings?
Ceramic bearings resist wear and heat better than steel. You get longer life and less friction. They cost more but work well in tough or dirty places.

 English
English