You can see the main difference between a ball bearing and a roller bearing by looking at how they touch. Ball bearings use point contact. Roller bearings use line contact. This small difference changes how they work in machines. For example, about 56% of the world uses ball bearings. Roller bearings make up 44%. Many engineers pick ball bearings for fast jobs. Ball bearings cause less surface change. They also work better at high speeds. E-ASIA makers often choose the right bearing based on speed and weight needs.

Key Takeaways
Ball bearings have small balls that touch at one spot. This makes them good for things that move fast.
Roller bearings have rollers that touch along a line. This helps them hold more weight.
Pick ball bearings for machines that need to spin quickly. They also help lower friction.
Use roller bearings for jobs that need a lot of strength. They last longer in tough work.
Ball bearings usually cost less money. They are also easier to take care of than roller bearings.
Think about how much weight your machine will carry. Also, check how fast it needs to go before you pick a bearing.
Ball bearings are found in things we use every day. You can see them in bikes and electric motors.
Roller bearings are used in big machines. You find them in conveyor belts and building equipment.
Ball Bearing Basics
Structure
A ball bearing has a simple design. It has four main parts. These are the inner ring, outer ring, balls, and cage. The balls go between the rings and roll when the bearing moves. The cage keeps the balls apart. This stops the balls from touching each other. The design helps the bearing work well and last longer.
You can see how ball bearings and roller bearings are different in this table:
Component | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
Rolling Elements | Small round balls | Rollers that are cylinder, tapered, or round |
Contact Area | Touches at one point | Touches along a line, spreads weight |
Load Capacity | Holds less weight | Holds more weight |
Applications | Used for fast spinning | Used for heavy loads |
Misalignment Tolerance | Works better if not lined up | Needs to be lined up well |
The balls touch the rings at one spot. This makes the bearing spin with little friction. Roller bearings use rollers that touch the rings in a line. This line contact spreads the weight out. Roller bearings can hold heavier loads.
How It Works
Ball bearings help parts move by lowering friction. The balls roll instead of slide. This makes moving easier. The balls hold the weight and let the inner ring turn inside the outer ring. The cage keeps the balls in place. It stops the balls from rubbing together.
Ball bearings are used in machines that spin fast. The point contact means less heat is made. This helps the bearing last longer and work well at high speeds. There is less damage, so you do not need to change the bearing often.
Materials
Ball bearings are made from different materials. The material depends on where you use them. Here is a table with common materials and their good points:
Material | Advantages | Best Industries/Applications |
Steel | Strong, lasts long, costs less | Factories, electric cars, warehouses |
Stainless Steel | Does not rust, stays strong, good for wet places | Medical, labs, food, wet places |
High-Performance Polymer | Handles heat, resists chemicals, does not carry electricity | Chips, medical, clean rooms |
Ceramic | Less friction, spins fast, not magnetic, works in heat | Needs quiet and less shaking |
Plastic | Light, does not need oil, does not rust | Used for normal or fast speeds |
Steel is used most for ball bearings. It is strong and lasts a long time. Stainless steel is good if you need no rust, like in food or medical tools. Ceramic bearings are quiet and spin fast. Plastic or polymer bearings are used when weight matters or chemicals might hurt metal.
When you choose a ball bearing, think about what the machine needs. For high speed, ceramic or steel is good. For no rust, pick stainless steel. Each material helps the bearing work better for its job.
Uses
You see ball bearings in many places every day. These bearings help things move smoothly and quietly. When you look at machines or devices that spin or rotate, you often find a bearing inside. Here are some common uses for ball bearings:
Electric Motors: You find ball bearings in fans, pumps, and power tools. The bearing lets the motor spin fast and last longer.
Bicycles: The wheels, pedals, and handlebars use bearings. This makes your ride smoother and easier.
Skateboards and Roller Skates: Each wheel has a bearing inside. You roll faster and with less effort because of this.
Home Appliances: Washing machines, blenders, and vacuum cleaners all use bearings. These parts help the machines run quietly and with less wear.
Automobiles: You see bearings in car wheels, engines, and transmissions. They reduce friction and help the car parts move well.
Computers and Office Equipment: Hard drives and printers use bearings. The bearing keeps the moving parts working smoothly.
Tip: If you hear a grinding or squeaking sound in a machine, the bearing might need to be replaced.
You also find ball bearings in many industrial machines. Factories use them in conveyor belts, robots, and assembly lines. The bearing helps these machines work faster and with less downtime. In medical devices, such as dental drills and small motors, the bearing allows for high-speed movement without much noise.
Here is a table that shows where you might find different types of bearings:
Application | Why Use a Bearing? | Type Used |
Bicycle Wheels | Smooth, fast spinning | Ball bearing |
Car Wheel Hubs | Handles weight and speed | Ball bearing |
Electric Fans | Quiet, long-lasting rotation | Ball bearing |
Conveyor Belts | Moves heavy loads | Roller bearing |
Skateboards | Fast, easy rolling | Ball bearing |
You should choose a ball bearing when you need something to spin quickly and with little friction. These bearings work best for light to medium loads. If you need to support a heavy load, you might pick a different type of bearing. Always check the needs of your machine before you choose a bearing.

Roller Bearing Basics
Structure
When you look at a roller bearing, you notice it has a different shape than a ball bearing. Instead of balls, you see rollers. These rollers can be cylindrical, tapered, or even needle-shaped. The rollers sit between an inner ring and an outer ring, just like in other bearings. A cage keeps the rollers spaced out so they do not touch each other. This design helps the bearing handle more weight.
Here is a table that shows how roller bearings and ball bearings differ in structure:
Feature | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
Rolling Elements | Spherical balls | Cylindrical, tapered, or needle-shaped rollers |
Load Capacity | Lower due to point contact | Higher due to line contact |
Applications | High-speed, low-torque | Heavy loads, lower speeds |
You can see that the main difference is the shape of the rolling elements. Ball bearings use round balls, while roller bearings use rollers. This change in shape gives the roller bearing a bigger contact area with the rings. Because of this, you get better support for heavy loads.
Ball bearings have spherical rolling elements.
Roller bearings use cylindrical, conical, or barrel-shaped rollers.
How It Works
A roller bearing works by letting the rollers move smoothly between the inner and outer rings. When you put weight on the bearing, the rollers spread the load over a larger area. This line contact means the bearing can handle more force without wearing out quickly. The cage keeps the rollers in place and stops them from rubbing against each other.
You often use a roller bearing when you need to support heavy loads. The rollers roll instead of slide, which lowers friction. This makes the bearing last longer, even in tough jobs. You might see roller bearings in machines that move slowly but carry a lot of weight, like conveyor belts or construction equipment.
Ball bearings are better for high-speed jobs because they have less friction. Roller bearings are better for heavy-duty work because they can take more weight.
Tip: If you need a bearing for a slow-moving but heavy machine, a roller bearing is usually the best choice.
Materials
You find roller bearings made from several materials. The choice of material affects how well the bearing works and how long it lasts. Here are some common materials used in roller bearings:
Chrome Steel: This is the most common material. It gives the bearing high hardness and good wear resistance. However, it does not resist rust well.
Stainless Steel: This material resists rust and corrosion. It is good for wet or harsh environments, but it is not as hard as chrome steel.
Carbon Alloy Steel: You see this in semi-precision bearings. It is less resistant to rust and often needs a protective coating.
Ceramic: Ceramic rollers are very hard and last a long time. They cost more but work well in special jobs.
Non-Metallic Materials: These include plastics and rubber. You find them in cages and seals. They are light and resist chemicals.
Here is a table that shows how each material affects bearing performance:
Material | Properties Impacting Performance |
Chrome Steel | High hardness, good wear resistance, but less corrosion resistance. |
Stainless Steel | Better corrosion resistance, lower hardness and load capacity. |
Carbon Alloy Steel | Used for semi-precision bearings, less corrosion resistant, often needs coatings. |
Ceramic | Very hard, used in hybrid bearings, more expensive. |
Non-Metallic Materials | Lightweight, used for cages and seals, chemical resistance. |
When you choose a roller bearing, think about where you will use it. For dry places, chrome steel works well. For wet or chemical areas, stainless steel or non-metallic materials are better. If you need a bearing that lasts a long time and can handle tough jobs, ceramic might be the right choice.
Uses
You find roller bearings in machines that carry heavy things. These bearings work well when you need to move big objects. They are good for jobs with a lot of weight. Ball bearings would not last long in these places.
Here are some ways people use roller bearings:
Conveyor Belts: Factories use these belts to move heavy items. Roller bearings help the belt roll even with lots of weight.
Elevators and Escalators: These machines lift people and things every day. The bearings inside keep the ride smooth and safe.
Construction Equipment: Cranes, bulldozers, and diggers all use roller bearings. These machines work with dirt, rocks, and heavy loads.
Railroad Cars and Locomotives: Trains carry huge loads for long trips. Roller bearings help the wheels turn with less rubbing and more power.
Wind Turbines: Wind turbines turn slowly but hold heavy blades. Roller bearings make this work.
Gearboxes: Many machines use gearboxes to change speed or direction. Roller bearings inside help the gears move easily.
Note: Pick a roller bearing if you need to hold a heavy load or want your machine to last longer when it works hard.
You also see these bearings in mining tools, paper mills, and steel plants. In these places, machines run for hours and face dust, heat, and shaking. Roller bearings help the machines keep working without breaking.
Here is a table that shows where you might use different roller bearings:
Application | Type of Roller Bearing | Why Use It? |
Conveyor Belt Rollers | Cylindrical | Handles heavy, steady loads |
Car Wheel Hubs | Tapered | Supports both weight and side force |
Wind Turbine Shafts | Spherical | Deals with misalignment and weight |
Mining Equipment | Needle | Fits in small spaces, carries load |
Always check what your machine needs before you pick a bearing. If you need to move something fast, a ball bearing may be better. If you need to carry a heavy load or deal with shaking, a roller bearing is the best choice.
Key Differences
Contact Type
When you look at a bearing, you notice how the parts touch each other. This is called the contact type. In a ball bearing, the balls touch the rings at just one point. This is called point contact. In a roller bearing, the rollers touch the rings along a line. This is called line contact.
You can see the difference in this table:
Bearing Type | Contact Type | Friction Level | Load Capacity | Suitable Applications |
Ball Bearing | Point Contact | Lower | Moderate | High-speed applications |
Roller Bearing | Line Contact | Higher | Higher | Heavy load applications |
Tip: If you want less friction and faster spinning, choose a ball bearing. If you need to carry more weight, a roller bearing works better.
Load Capacity
Load capacity tells you how much weight a bearing can hold. You need to think about this when you pick a bearing for your machine. Ball bearings can handle moderate loads. Roller bearings can handle much heavier loads because the rollers spread the weight over a bigger area.
Here is a table that shows how load capacity compares:
Bearing Type | Load Capacity | Typical Applications |
Roller Bearing | Higher radial load capacity | Heavy machinery, conveyor belts, automotive drivetrains |
Ball Bearing | Lower radial load capacity | Small-scale electric motors, pumps, household appliances |
You use a ball bearing when your machine does not need to carry much weight. You use a roller bearing when you need to move heavy things or support big machines. The line contact in a roller bearing helps it last longer under heavy loads.
Speed Suitability
Speed suitability means how fast a bearing can spin without problems. Ball bearings work best at high speeds. They have less friction because of the point contact. This makes them perfect for things like electric motors and fans. Roller bearings can spin, but they work better at lower speeds. The line contact creates more friction, so they are not as good for fast spinning.
Look at this table to compare speed:
Bearing Type | Max Speed Limit | Friction Coefficient | Typical Applications |
Ball Bearing | Up to 30,000 RPM | 0.001–0.0015 | Electric motors, fans |
Roller Bearing | Up to 12,000 RPM | 0.002–0.004 | Gearboxes, conveyors, trucks |
Note: If your machine needs to spin very fast, pick a ball bearing. If you need to carry a heavy load at a slower speed, use a roller bearing.
Cost
When you choose a bearing, you need to think about cost. The price of a bearing depends on its type, size, material, and how much weight it can hold. Ball bearings usually cost less than roller bearings. You see this difference because ball bearings have a simpler design and use fewer materials.
A roller bearing often costs more. The reason is that it has a larger contact area and can handle higher load capacity. You pay more for a roller bearing if you need it to support heavy machines or work in tough places. The extra cost gives you better strength and longer life for your equipment.
Here is a table to help you compare the cost factors:
Factor | Ball Bearing | Roller Bearing |
Design Complexity | Simple | More complex |
Material Needed | Less | More |
Load Capacity | Lower | Higher |
Average Cost | Lower | Higher |
Maintenance Cost | Lower | Can be higher |
Tip: If your machine does not need to carry a heavy load, you can save money by choosing a ball bearing. If you need more load capacity and longer life, a roller bearing is worth the higher price.
You also need to think about long-term costs. A cheaper bearing might wear out faster and need more replacements. A more expensive bearing with higher load capacity can last longer and save you money over time. Always match the cost to your needs. Do not pay for extra strength if you do not need it.
Some industries pick roller bearings even though they cost more. They do this because the machines must carry heavy loads every day. In other cases, you can use a ball bearing and keep your costs low.
Pros and Cons
Ball Bearing Advantages
Ball bearings help machines run smoothly. They make equipment last longer. These bearings lower friction. This means machines use less energy. You save money on energy and repairs. Ball bearings fit many machines. You see them in bikes and motors. They are simple to put in and take out. You do not need special tools.
You can check the table for more details:
Advantage | Benefit |
Reduced Friction | Saves energy while the machine works. |
| Costs less to run and needs less power. |
Durability | Stays strong and does not break easily. |
| Machines last longer and need fewer fixes. |
Versatility | Works in many kinds of machines and jobs. |
| Can be used for different needs in factories. |
Tip: Good ball bearings help you save energy and money over time.
Ball Bearing Disadvantages
Ball bearings have some limits you should know. They cannot hold very heavy things. If you put too much weight, they might break. They do not work well if the machine shakes a lot. Ball bearings can get noisy if dirty or not cared for. You may need to change them more often in hard places.
If your machine carries heavy things or gets hit hard, pick another bearing.
Roller Bearing Advantages
Roller bearings are strong for moving heavy stuff. They have special features for tough jobs. Roller bearings hold more weight than ball bearings. The line contact spreads the weight out. This helps the bearing last longer. There are many roller bearing types. You can pick cylindrical, needle, tapered, or spherical. Each type fits a different job. Some roller bearings work even if not lined up right. Spherical roller bearings handle misalignment. These bearings are good for machines that get hit or face shocks.
See the table for roller bearing advantages:
Type of Roller Bearing | Advantages |
Standard Cylindrical Roller Bearing | Holds more weight, comes in single, double, or multi-row. |
Needle Roller Bearing | Fits small spaces, best for slow-moving machines. |
Tapered Roller Bearings | Handles side force, takes more weight with bigger taper. |
Spherical Roller Bearings | Good for heavy shocks, works even if not lined up. |
Note: If your machine needs to carry lots of weight or faces strong hits, roller bearings are usually the best choice.
Roller Bearing Disadvantages
When you choose a roller bearing, you get strength and durability. However, you also face some drawbacks. You need to know these before you decide if this type of bearing fits your needs.
Lower Speed Limits
Roller bearings do not work well at very high speeds. The rollers create more friction than balls. This extra friction can cause heat. If you use a roller bearing in a fast-spinning machine, it may wear out quickly or even fail.
More Noise and Vibration
You might notice that machines with roller bearings make more noise. The line contact between the rollers and the rings can cause vibration. This can lead to louder operation, especially if the bearing is not installed perfectly.
Higher Cost
Roller bearings often cost more than ball bearings. The design is more complex. You pay more for the extra strength and load capacity. If your machine does not need to carry heavy loads, you might spend more money than needed.
Larger Size and Weight
These bearings are usually bigger and heavier than ball bearings. If you have limited space or need a lightweight design, a roller bearing may not fit well. The extra size can also make installation harder.
Sensitive to Misalignment
Most roller bearings need perfect alignment. If the shaft or housing is not straight, the bearing can wear out faster. Some types, like spherical roller bearings, handle misalignment better, but most do not.
Note: If you do not install the bearing correctly, you may face early failure or more maintenance.
Here is a table to help you see the main disadvantages:
Disadvantage | What It Means for You |
Lower speed limits | Not good for fast-spinning machines |
More noise and vibration | Machines may sound louder |
Higher cost | You pay more for extra strength |
Larger size and weight | Harder to fit in small spaces |
Sensitive to alignment | Needs careful installation |
More maintenance | Takes more time and effort to check |
You should always match the bearing to your machine’s needs. If you do not need to carry heavy loads, a ball bearing might be a better choice. Think about speed, space, and cost before you pick a roller bearing.
Load and Speed
Radial and Axial Loads
When you pick a bearing, you must know what loads it can take. Radial loads push down on the bearing. Axial loads push along the shaft. Some machines need to handle both at once. Ball bearings and roller bearings are good for different jobs.
You can see how they compare in this table:
Type of Bearing | Radial Load Capacity | Axial Load Capacity | Combined Load Capacity |
Ball Bearings | Moderate to high, depending on bearing size and design. | Moderate, but some designs can handle higher axial loads with proper arrangements like angular contact ball bearings. | Can handle combined radial and axial loads to varying degrees, depending on design. |
Roller Bearings | High, especially for cylindrical and tapered roller bearings. | Moderate to high, depending on bearing type and arrangement. | Can handle combined radial and axial loads efficiently, especially spherical roller bearings and tapered roller bearings. |
Roller bearings are best for heavy radial loads. Tapered and spherical types also handle strong axial forces. Ball bearings can take both loads, but they do better with lighter weights. If your machine needs to handle both forces, check the bearing’s design before you choose.
Tip: For machines that push and pull, tapered roller bearings or angular contact ball bearings work well.
High-Speed Performance
Speed is important for many machines. Some bearings spin faster than others. Ball bearings are good for high speeds. They make less friction. Roller bearings can spin fast too, but they have more friction because of their bigger contact area.
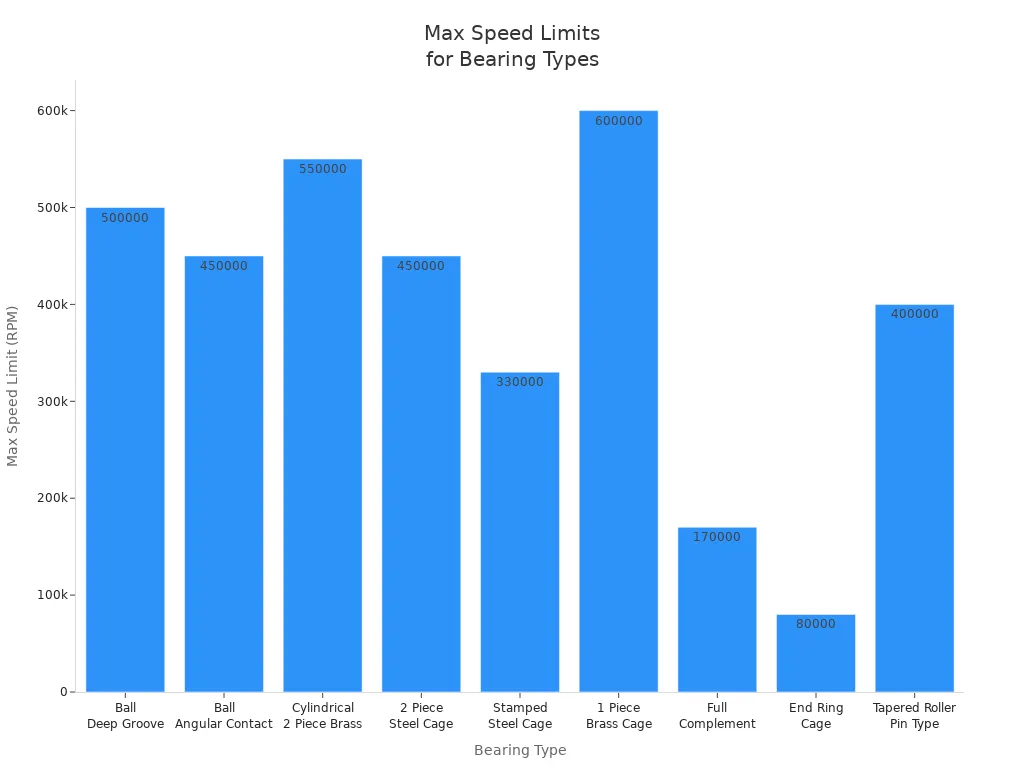
Here is a table with speed limits for each type:
Bearing Type | Speed Limit (RPM) |
Ball, Deep Groove | 500,000 |
Ball, Angular Contact | 450,000 |
Cylindrical, 2 Piece Brass Cage | 550,000 |
2 Piece Steel Cage | 450,000 |
Stamped Steel Cage | 330,000 |
1 Piece Brass Cage | 600,000 |
Full Complement | 170,000 |
End Ring Cage | 80,000 |
Tapered Roller, Pin Type Cage | 400,000 |
Some ball bearings can spin up to 500,000 RPM. Roller bearings like tapered or cylindrical types can also go fast, but not as fast as ball bearings. If your machine spins very fast, pick a bearing made for speed.
Note: Always check the speed rating before using a bearing in a fast machine.
Durability
You want your machine to last a long time. How long a bearing lasts depends on its type and use. Roller bearings usually last longer than ball bearings if used the same way. This is because roller bearings spread the load out more.
Here is a table with average lifespans:
Bearing Type | L10 Life (hours) |
Ball Bearing | 34,000 |
Roller Bearing | 71,000 |
A roller bearing can last more than twice as long as a ball bearing in the same job. This means you will have less downtime and fewer replacements.
Tip: Take care of your bearings and install them right to help them last longer.
Applications
Ball Bearing Applications
Ball bearings help machines move fast and smooth. They lower friction and support different loads. You see them in things that spin quickly. Some examples are electric motors, fans, and printers. Bicycles and skateboards use ball bearings too. Car engines and transmissions need them. Wind turbines and pumps also use ball bearings.
Ball bearings make machines quiet and last longer. They help machines work well, even with heavy loads. Many industries use ball bearings for different jobs. Here is a table that shows where ball bearings are used:
Industry | Typical Applications |
Mechanical Engineering | Wind turbines, electric motors, gearboxes, pumps, fans, drive shafts |
Automotive | Engines, transmission systems, suspension systems, wheel hub assemblies |
Electronic Equipment | Printers, optical devices, electronic fans |
Agricultural Machinery | Tractors, plows, harvesters |
Aerospace | Aircraft, helicopters, spacecraft |
Ball bearings have two rings and steel balls inside. This design lowers friction and helps things move smoothly in motors, wheels, and transmissions.
Roller Bearing Applications
Roller bearings hold heavier loads than ball bearings. You use them in machines that carry big weights or face strong forces. These bearings work best in slow machines where strength is important. Some examples are conveyor belts and gearboxes. Motors in vehicles use roller bearings. Construction machines like cranes and drills need them. Wind turbines and oil pumps use roller bearings too. Steel mills and material handling machines also need them.
Roller bearings come in different shapes for special jobs. Some are cylindrical, tapered, or spherical. Here is a table that shows where roller bearings are used:
Industry | Typical Applications |
Power Generation | Wind turbines, oil pumps |
Automotive | Gearboxes, motors, off-road vehicles |
Manufacturing | Steel mills, material handling, food processing machines |
Construction | Construction machinery, drilling units |
HVAC | Air conditioning compressors |
Household | Kitchen faucets |
Marine | Marine propulsion |
Pulp and Paper | Pulp processing equipment |
If your machine needs to carry heavy weight or work hard, roller bearings are a good choice.
Industry Examples
Bearings are used in almost every industry. They help machines work better and last longer. Industrial machines use bearings for heavy jobs. Aerospace equipment needs bearings to lower friction and hold big weights. Robots and automation use bearings for smooth movement. Power plants use bearings in turbines and generators for steady work.
Bearings help machines run safely and smoothly. Picking the right bearing helps your equipment last longer and work better.
Choosing Bearings
Factors
When you select the right bearing for your machine, you need to look at a few important factors. Each type of bearing works best in certain situations. You should think about how much weight the bearing must hold, how fast it will spin, and where you will use it. The table below can help you compare ball bearings and roller bearings:
Bearing Type | Load Capacity | Speed Capability | Applications |
Roller Bearings | Higher radial loads | Lower speeds | Industrial machinery, automotive, aerospace |
Ball Bearings | Lower loads | High speeds | Applications with limited space and high-speed needs |
You should also consider the space you have in your design. Ball bearings fit well in small spaces and work best when you need high speed. Roller bearings are better for heavy loads and tough jobs. Always match the bearing to the needs of your machine.
Ball vs. Roller Comparison
Features
When you look at a ball bearing and a roller bearing, you notice they work differently. Each type is good for certain jobs. You should check how each bearing handles contact, load, and movement.
Here is a table that shows the main features side by side:
Feature | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
Contact Type | Point contact, resulting in low friction | Line contact, providing larger surface area |
Load Capacity | Lower capacity, better for lighter loads | Higher capacity, suitable for heavier loads |
Design | Spherical balls, versatile in rotation | Cylindrical rollers, available in various shapes |
Application Suitability | Best for high-speed, low-load applications | Better for high-load and shock resistance |
A ball bearing uses small balls. These balls touch the rings at one spot. This design makes less friction. It helps things spin fast. A roller bearing uses rollers. The rollers touch the rings along a line. This spreads out the weight. It lets the bearing hold more load.
Tip: Pick a ball bearing for less friction and high speed. Choose a roller bearing for heavy weight or strong shocks.
Summary
You should pick the right bearing for your machine. Think about the load, speed, and space you need. Here is a summary table to help you decide:
Feature | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
Load Capacity | Limited capacity for heavy radial loads | Higher load capacity due to line contact |
Friction Coefficient | Lower, ideal for high-speed applications | Higher, may affect speed in some applications |
Durability | Can deform under excessive loads | More robust, handles heavier loads without deforming |
Size | Compact design, requires less space | Generally bulkier, requires more space |
Maintenance | Low maintenance in less axial load applications | May require more frequent maintenance |
Sensitivity | More vulnerable to misalignment and shock loads | Less sensitive to shock loads and misalignment |
Versatility | Suitable for both radial and axial loads | Variety of designs for different applications |
Note: Always choose the bearing that fits your machine’s needs. The right bearing helps your equipment work better and last longer.
You now understand how ball bearings and roller bearings are different. Ball bearings have round balls inside. They work best for fast and light jobs. You see them in things like bikes and washing machines. Roller bearings use rollers instead of balls. They are good for heavy jobs and tough places. Gearboxes often use roller bearings. When you pick a bearing, look at the weight it must hold. Check how fast it needs to spin. Think about where you will use it. Use this table to help you choose:
Criteria | Ball Bearings | Roller Bearings |
Speed | High | Lower |
Load Capacity | Lower | Higher |
Best Use | Everyday machines | Heavy machinery |
Remember: Always pick the bearing that fits your machine’s job. This helps your machine work better.
FAQ
What is the main difference between ball bearings and roller bearings?
You see the main difference in how they touch. Ball bearings use balls for point contact. Roller bearings use rollers for line contact. This changes how much weight each can hold and how fast they can spin.
Can you use ball bearings and roller bearings in the same machine?
You can use both types in one machine if the design needs it. For example, you might use ball bearings for fast-spinning parts and roller bearings for heavy loads in the same system.
How do you know which bearing to choose?
You should look at the load, speed, and space in your machine. Ball bearings work best for high speed and light loads. Roller bearings fit heavy loads and slower speeds. Always check your machine’s needs first.
Do ball bearings need more maintenance than roller bearings?
You usually spend less time on ball bearing maintenance. Roller bearings may need more checks because they handle heavier loads and can wear faster if not aligned well.
Are ceramic bearings better than steel bearings?
Ceramic bearings spin faster and resist heat. They cost more than steel bearings. You should use ceramic if you need high speed or less friction. Steel works well for most everyday uses.
What happens if you use the wrong bearing?
If you pick the wrong bearing, your machine may break or wear out quickly. You might hear noise, feel vibration, or see damage. Always match the bearing to your machine’s job.
Can you replace a ball bearing with a roller bearing?
You can sometimes swap them, but not always. Roller bearings are bigger and need more space. Check your machine’s design and size before you make a change.
How do you know when a bearing needs to be replaced?
You might hear grinding or squeaking. You may feel extra heat or see the machine slow down. If you notice these signs, you should check and replace the bearing soon.

 English
English